- Payment Options
- Terms Conditions
- Malibu 453 blv
- info@charity.com
Notice: Test mode is enabled. While in test mode no live donations are processed.
Hindutva extremism is a growing ideological movement that promotes a Hindu nationalist agenda, often at the expense of minorities, democratic values, and secularism. While Hindutva originated in India, its influence has expanded globally, including in Australia, where it poses challenges to social harmony, multiculturalism, and civil rights. This article explores the global implications of Hindutva extremism, its oppression of Indian minorities, and its conflict with Australian shared values.
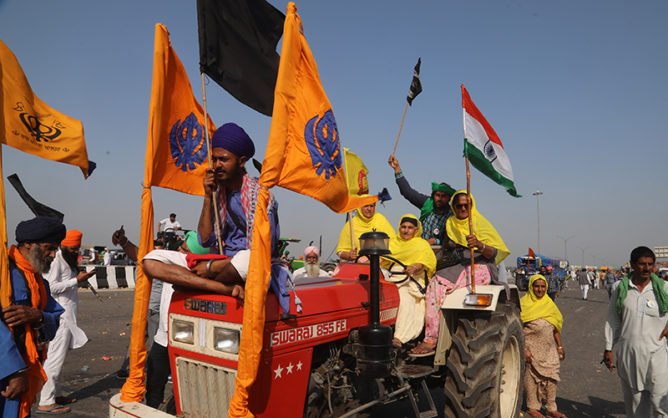

Hindutva ideology, championed by groups like the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), Vishva Hindu Parishad (VHP), and Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), has led to rising communal tensions worldwide. The movement’s influence has been seen in:
• Diaspora Radicalization: Pro-Hindutva organizations have gained traction in countries like the UK, Canada, and Australia, where they spread anti-minority propaganda and attempt to influence political discourse.
• Export of Hate Crimes: Reports of violence against Sikhs, Muslims, and Dalits by Hindutva-affiliated individuals in the diaspora have increased. In Leicester (UK), in 2022, Hindutva mobs attacked Muslim neighborhoods, exposing their growing reach.
• Targeting Academic and Media Institutions: Hindutva groups have tried to silence critics, attacking university professors, journalists, and activists who challenge their ideology. In Australia, they have pressured institutions to alter historical narratives that highlight Indian pluralism.
Hindutva extremism systematically marginalizes and oppresses non-Hindu communities in India. These oppressive practices have direct implications for Indian-origin communities in Australia who seek safety and freedom. Examples include :
• 1984 Sikh Genocide Denial: Hindutva nationalists continue to whitewash the genocide of Sikhs in India, spreading disinformation in global forums.
• Persecution of Muslims: The introduction of the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) and the National Register of Citizens (NRC) systematically discriminates against Muslims. This ideological hostility has been mirrored in Australia, where Hindutva groups have opposed Muslim immigrants.
• Violence Against Dalits and Christians: Caste-based oppression remains rampant, with Hindutva forces engaging in mob violence against Dalits and Christian minorities. Some Australian-based Dalit activists have faced intimidation from Hindutva-linked individuals.
Australia’s multicultural democracy is built on inclusivity, secularism, and freedom of expressionall of which are under threat from Hindutva extremism. The ideology directly contradicts Australian principles by:
To protect its democratic values and minority communities, Australia must take proactive steps against Hindutva extremism. Key actions include:
o Recognize Hindutva extremism as a form of political radicalization and monitor organizations with direct links to RSS/VHP/BJP.
o Strengthen hate crime laws to protect Sikhs, Muslims, Dalits, and Christians from Hindutva-driven violence.
o Support academic research that exposes Hindutva influence in diaspora politics.
o Encourage interfaith and intercultural dialogues to promote true inclusivity and challenge divisive narratives.
o Investigate and restrict foreign funding from extremist Hindutva-affiliated groups into Australian temples and cultural organizations.
o Monitor and dismantle hate-driven social media networks promoting communal propaganda.
Hindutva extremism is not just an Indian problem, it’s a global issue that threatens social harmony and democracy, including in Australia. By raising awareness, pushing for governmental action, and strengthening community resistance, Australians can uphold their shared values of justice, secularism, and human rights. The Sikh community and other marginalized groups must continue leading the charge against Hindutva extremism, ensuring Australia remains a safe and inclusive country for all.
1. Human Rights Watch – Reports on Hindutva violence and suppression of minorities.
2. Amnesty International – Investigations into Indian human rights violations.
3. Australian Government Reports – Hate crimes and extremism monitoring.
4. Academic Research – Hindutva’s impact on global politics and diaspora communities.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit aenean comm odo ligula eget dolor massa Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Aenean egestas magna at porttitor vehicula nullam.